keras 버젼은 아래를 참조
[deep learning] 2. Fashion MNist (keras 버젼)
목적1. 이미지 데이터의 분류(classification)2. 학습 데이터의 가공 방법3. 모델의 문제점 분석과 개선 전략 데이터셋 패션_엠니스트 | TensorFlow Datasets이 페이지는 Cloud Translation API를 통해 번역되었습
eldercoder.tistory.com
1. 패키지 설치
| pip install torch pip install torchvision |
2. 임포트
|
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim # Changed from torch.optim to torch.optim as optim for clarity
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
|
3. Fashion MNIST 데이터 로드 및 전처리
|
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) # Fashion MNIST is grayscale, so one channel (mean, std)
])
# Load Fashion MNIST training dataset
train_dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root='./data',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transform
)
# Load Fashion MNIST test dataset
test_dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root='./data',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=transform
)
# Create DataLoaders
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=False)
|
4. 모델클래스 정의
|
class FashionCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FashionCNN, self).__init__()
self.conv_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# Calculate the output size of the convolutional layers
# Input: 1x28x28. After first Conv2d (32x28x28) -> MaxPool (32x14x14)
# After second Conv2d (64x14x14) -> MaxPool (64x7x7)
self.fc_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(64 * 7 * 7, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(128, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_layers(x)
x = self.fc_layers(x)
return x
|
5. 모델클래스 인스턴스화
| # Instantiate the model model = FashionCNN() # Move model to GPU if available device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") model.to(device) |
6. 학습용 로스함수 옵티마이저
|
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001) |
7. 학습
|
num_epochs = 10
train_losses = []
train_accuracies = []
val_losses = []
val_accuracies = []
# Early Stopping 관련 변수 초기화
best_val_loss = float('inf')
patience_counter = 0
patience = 5 # 5 에포크 동안 검증 손실 개선이 없으면 중단
best_model_state = None
best_model_path = 'pytorch_early_stopping_best_model.pth' # 최적 모델 저장 경로
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train() # Set the model to training mode
running_loss = 0.0
correct_train = 0
total_train = 0
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad() # Zero the parameter gradients
outputs = model(images) # Forward pass
loss = criterion(outputs, labels) # Calculate loss
loss.backward() # Backward pass
optimizer.step() # Optimize
running_loss += loss.item()
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total_train += labels.size(0)
correct_train += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
epoch_train_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
epoch_train_accuracy = 100 * correct_train / total_train
train_losses.append(epoch_train_loss)
train_accuracies.append(epoch_train_accuracy)
# Validation phase
model.eval() # Set the model to evaluation mode
val_running_loss = 0.0
correct_val = 0
total_val = 0
with torch.no_grad(): # Disable gradient calculation for validation
for images, labels in test_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
val_loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
val_running_loss += val_loss.item()
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total_val += labels.size(0)
correct_val += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
epoch_val_loss = val_running_loss / len(test_loader)
epoch_val_accuracy = 100 * correct_val / total_val
val_losses.append(epoch_val_loss)
val_accuracies.append(epoch_val_accuracy)
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], '
f'Train Loss: {epoch_train_loss:.4f}, Train Accuracy: {epoch_train_accuracy:.2f}%, '
f'Validation Loss: {epoch_val_loss:.4f}, Validation Accuracy: {epoch_val_accuracy:.2f}%')
# Early Stopping 로직
if epoch_val_loss < best_val_loss:
best_val_loss = epoch_val_loss
patience_counter = 0
best_model_state = copy.deepcopy(pytorch_early_stopping_model.state_dict()) # 최적 모델 상태 저장
torch.save(best_model_state, best_model_path) # 최적 모델 가중치 파일로 저장
print(f' Validation loss improved. Saving best model state to {best_model_path}. Best loss: {best_val_loss:.4f}')
else:
patience_counter += 1
print(f' Validation loss did not improve. Patience counter: {patience_counter}/{patience}')
if patience_counter >= patience:
print(f' Early stopping triggered after {patience} epochs of no improvement.')
break
# 학습 종료 후 최적의 모델 가중치 로드
if best_model_state:
# 파일에서 직접 로드할 수도 있습니다.
# pytorch_early_stopping_model.load_state_dict(torch.load(best_model_path))
model .load_state_dict(best_model_state)
print("Best model weights restored for PyTorch model.")
학습이 완료된 PyTorch 모델(model)의 상태 사전(state_dict)을 파일로 저장합니다.
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'pytorch_fashion_mnist_cnn.pth')
|
8. 학습과정 시각화
|
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(train_accuracies, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(val_accuracies, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(train_losses, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_losses, label='Validation Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
|

9. 모델 평가
|
model.eval() # Set the model to evaluation mode
test_loss = 0.0
correct_test = 0
total_test = 0
with torch.no_grad(): # Disable gradient calculation
for images, labels in test_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
test_loss += loss.item()
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total_test += labels.size(0)
correct_test += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
final_test_loss = test_loss / len(test_loader)
final_test_accuracy = 100 * correct_test / total_test
print(f'Test Loss: {final_test_loss:.4f}')
print(f'Test Accuracy: {final_test_accuracy:.4f}%')
|
Test Loss: 0.2298
Test Accuracy: 91.8900%
10. 클래스별 세부 성능 분석
|
y_true_pytorch = []
y_pred_pytorch = []
model.eval() # Set model to evaluation mode
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
y_true_pytorch.extend(labels.cpu().numpy())
y_pred_pytorch.extend(predicted.cpu().numpy())
# Convert lists to numpy arrays
y_true_pytorch = np.array(y_true_pytorch)
y_pred_pytorch = np.array(y_pred_pytorch)
# Generate a classification report
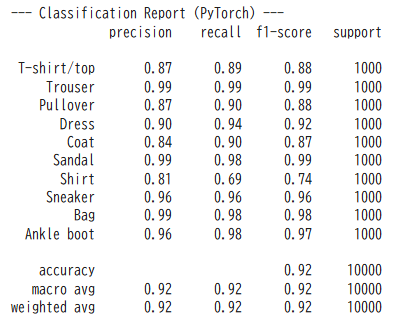
print("\n--- Classification Report (PyTorch) ---")
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
print(classification_report(y_true_pytorch, y_pred_pytorch, target_names=class_names))
# Generate and display the confusion matrix
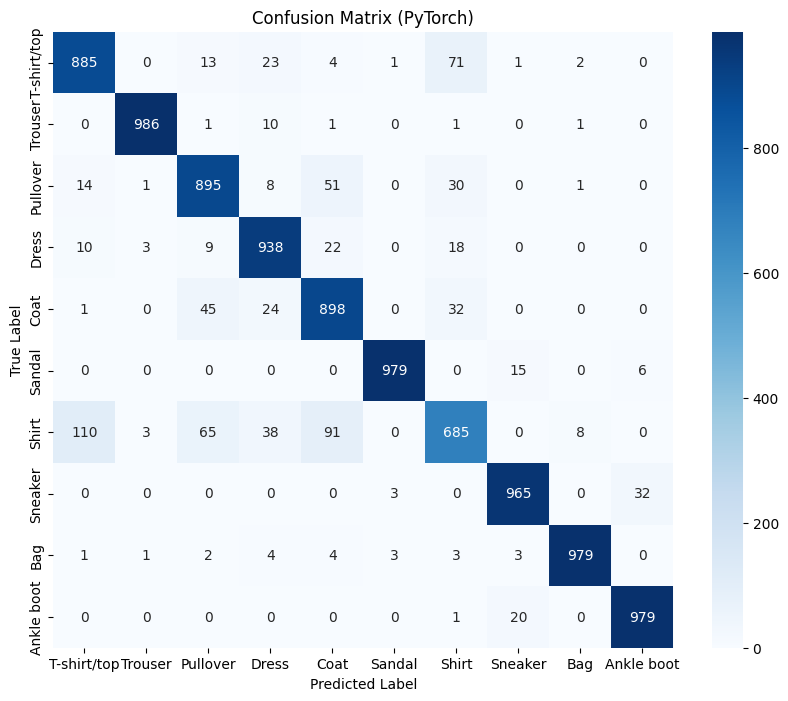
print("\n--- Confusion Matrix (PyTorch) ---")
cm_pytorch = confusion_matrix(y_true_pytorch, y_pred_pytorch)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
sns.heatmap(cm_pytorch, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues', xticklabels=class_names, yticklabels=class_names)
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')
plt.ylabel('True Label')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix (PyTorch)')
plt.show()
|
11. 학습된 모델 화일을 로드하여 추론
|
# 1. 새로운 PyTorch 모델 인스턴스(loaded_pytorch_model)를 생성합니다.
loaded_pytorch_model = FashionCNN() # 2. 저장된 상태 사전 파일을 불러와 loaded_pytorch_model에 로드합니다. loaded_pytorch_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('pytorch_fashion_mnist_cnn.pth')) # 3. loaded_pytorch_model.eval()을 호출하여 모델을 평가 모드로 설정합니다. loaded_pytorch_model.eval() # 4. loaded_pytorch_model을 device (CPU 또는 GPU)로 이동시킵니다. loaded_pytorch_model.to(device) # 5 torch.no_grad() 컨텍스트 내에서 예측을 수행하여 그라디언트 계산을 비활성화합니다.
with torch.no_grad():
images = images.to(device) outputs = loaded_pytorch_model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
|
'data science > Artificial Intelligence' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [deep learning] 2. Fashion MNist (keras 버젼) (0) | 2026.02.06 |
|---|---|
| [deep learning] 1. Combined Cycle Power Plant (keras 버젼) (0) | 2026.02.06 |
| Transformer (GPT) 가장 쉽게 이해하기 - Part 2 (0) | 2025.10.26 |
| Transformer (GPT) 가장 쉽게 이해하기 - Part 1 (0) | 2025.10.19 |
| SVM(Support Vector Machines) Classifier (0) | 2025.04.02 |