목적
과거 발전소에서의 조건 [AT: 시간당 평균 온도] [V: 배기진공] [AP: 주위 압력] [RH: 습도] 에 따라 출력 [PE] 데이터를 학습하므로써 새로운 조건에 따라서 예상 출력을 예측하는 모델의 구축.
데이터셋
UCI Machine Learning Repository
This dataset is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. This allows for the sharing and adaptation of the datasets for any purpose, provided that the appropriate credit is given.
archive.ics.uci.edu
1. 패키지 설치
|
pip install keras
pip install tensorflow
pip install openpyxl
|
2. 임포트
|
import keras
from keras.layers import Dense, Input
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
|
3. 데이터셋을 pandas 에 다운로드
|
file_path = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/billcary/uci_combined_cycle_power_plant/master/data/Folds5x2_pp.xlsx'
df = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name='Sheet1')
|
4. 데이터셋의 내용 (df.head(3))
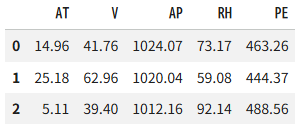
5. 입력값(=X)과 출력값(=Y) 분리
|
X, Y = df[ ["AT", "V", "AP", "RH"] ], df["PE"]
|
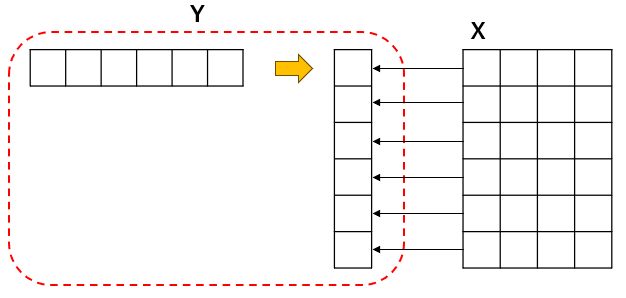
6. 구조(shape)의 동일화
X 는 2차원구조로 횡으로 9568인덱스를 가지고 각열은 4개의 데이터를 가지고 있다.
하지만 Y는 열로 9568의 데이터를 가지고 있다.
이를 X와 대응하는 구조로 바꿀 필요가 있기 때문에
|
Y = Y.values.reshape(-1,1)
|
reshape 의 첫번째를 -1 를 해줌으로써 두번째에 맞춰 자동으로 종과 횡 형태의 (9568, 1) 로 변환하게 된다.
7. 데이터의 정규화(Normalization)
데이터를 작게 만들어 모델의 학습 속도, 안정성, 그리고 성능(Generalization)에 직면한 여러 문제들을 해결하기 위해 필요
|
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_new = scaler.fit_transform(X)
target_scaler = MinMaxScaler()
Y_new = target_scaler.fit_transform(Y)
|
8. 학습용 / 테스트 데이터 분리 (4할)
|
X_train, X_test, Y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_new, Y_new, test_size=0.4, random_state=333)
|
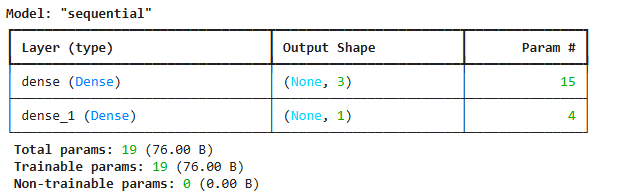
9. 모델 정의
4개의 입력을 받아 3개로 줄인 후 마지막 데이터 1개를 출력
|
regressor = keras.Sequential()
regressor.add(Input(shape=(X_train.shape[1],))) // = 4
regressor.add(Dense(3))
regressor.add(Dense(1))
|
10. 모델에 학습 최적화방법(optimizer) 와 로스함수(loss) 설정
|
regressor.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mse')
|
11. 학습(training)
|
history = regressor.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=50)
|
X_train : 학습데이터 [ [ , , , ] [ , , , ] ....]
Y_train : 정답데이터 [ [ ] [ ] ...]
batch_size : 파라미터들이 학습(업데이트)되는 데이터들의 묶음 단위
epochs : X_train 데이터 재 학습 횟수
12. 학습결과 분석
이번 모델은 분류(classification)가 아니라 회귀(regression 연속적인 수취예측) 이기 때문에 accuracy 는 구할 수 없고 loss 만 구할 수 있다.
|
loss = history.history['loss']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(epochs, loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss over Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|

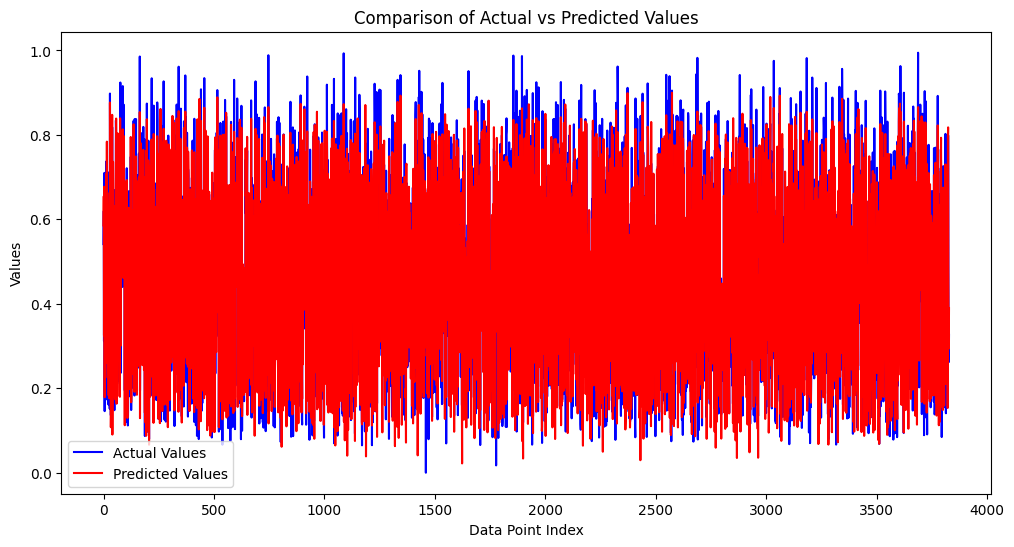
13. 테스트 데이터로 모델의 성능을 측정
|
y_pred = regressor.predict(X_test)
x_range = range(len(y_test))
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(x_range, y_test, 'b-', label='Actual Values')
plt.plot(x_range, y_pred, 'r-', label='Predicted Values')
plt.title('Comparison of Actual vs Predicted Values')
plt.xlabel('Data Point Index')
plt.ylabel('Values')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|
'data science > Artificial Intelligence' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [deep learning] 2. Fashion MNist (pytorch 버젼) (0) | 2026.02.07 |
|---|---|
| [deep learning] 2. Fashion MNist (keras 버젼) (0) | 2026.02.06 |
| Transformer (GPT) 가장 쉽게 이해하기 - Part 2 (0) | 2025.10.26 |
| Transformer (GPT) 가장 쉽게 이해하기 - Part 1 (0) | 2025.10.19 |
| SVM(Support Vector Machines) Classifier (0) | 2025.04.02 |