|
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv(data_path, header=None, sep='::', engine='python')
df.columns = ['user_id', 'movie_id', 'rating', 'timestamp']
|
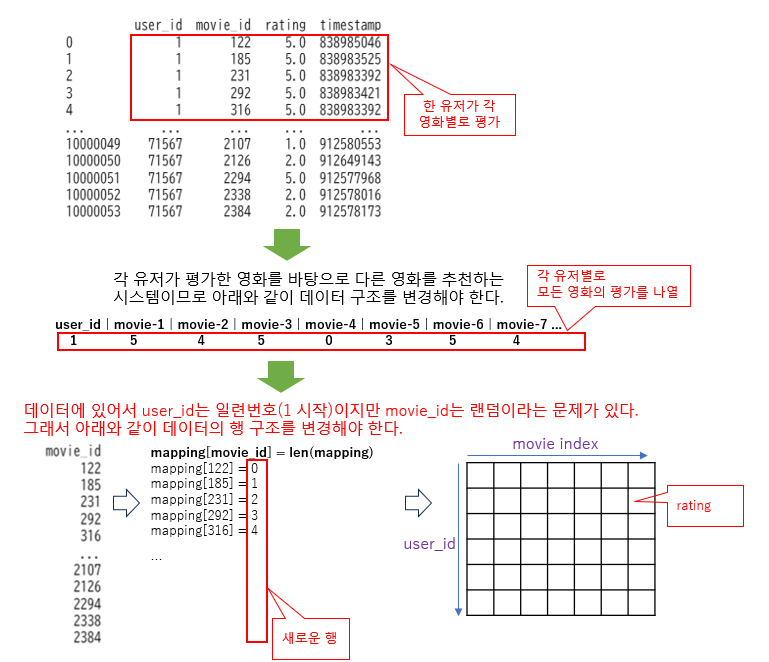
|
n_users = df['user_id'].nunique()
n_movies = df['movie_id'].nunique()
def load_user_rating_data(df, n_users, n_movies):
data = np.zeros([n_users, n_movies], dtype=np.intc)
movie_id_mapping = {}
for user_id, movie_id, rating in zip(df['user_id'], df['movie_id'], df['rating']):
user_id = int(user_id) - 1
if movie_id not in movie_id_mapping:
movie_id_mapping[movie_id] = len(movie_id_mapping)
data[user_id, movie_id_mapping[movie_id]] = rating
return data, movie_id_mapping
data, movie_id_mapping = load_user_rating_data(df, n_users, n_movies)
# rating별 통계계
values, counts = np.unique(data, return_counts=True)
for value, count in zip(values, counts):
print(f'Number of rating {value}: {count}')
# movie_id별 통계계
print(df['movie_id'].value_counts())
|
| Number of rating 0: 21384031 Number of rating 1: 56174 Number of rating 2: 107557 Number of rating 3: 261197 Number of rating 4: 348971 Number of rating 5: 226310 2858 3428 260 2991 1196 2990 1210 2883 480 2672 ... 3458 1 2226 1 1815 1 398 1 2909 1 Name: movie_id, Length: 3706, dtype: int64 |
movie_id = 2858을 대상으로 추천을 할지 안할지를 알아보자.
즉 데이터셋에서 movie_id = 2858 를 제거한 상태
|
target_movie_id = 2858
X_raw = np.delete(data, movie_id_mapping[target_movie_id], axis=1)
Y_raw = data[:, movie_id_mapping[target_movie_id]]
X = X_raw[Y_raw > 0]
Y = Y_raw[Y_raw > 0]
print('Shape of X:', X.shape)
print('Shape of Y:', Y.shape)
|
|
Shape of X: (3428, 3705)
Shape of Y: (3428,) |
추천(=1), 비추천(=0)으로 이진화하기 위해 rating을 3을 기준으로 타켓을 변환
|
recommend = 3
Y[Y <= recommend] = 0
Y[Y > recommend] = 1
n_pos = (Y == 1).sum()
n_neg = (Y == 0).sum()
print(f'{n_pos} positive samples and {n_neg} negative samples.')
|
|
2853 positive samples and 575 negative samples.
|
준비된 데이터세을 8:2 로 학습용과 테스트용으로 분리
|
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
print(len(Y_train), len(Y_test))
|
|
2742 686
|
Naïve Bayes 트레이닝
|
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
clf = MultinomialNB(alpha=1.0, fit_prior=True)
clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
|
Accuracy(정확도) 체크
|
prediction_prob = clf.predict_proba(X_test)
print(prediction_prob[0:10])
prediction = clf.predict(X_test)
print(prediction[:10])
print(Y_test[:10]) accuracy = clf.score(X_test, Y_test)
print(f'The accuracy is: {accuracy*100:.1f}%')
|
|
[[7.50487439e-23 1.00000000e+00]
[1.01806208e-01 8.98193792e-01] [3.57740570e-10 1.00000000e+00] [1.00000000e+00 2.94095407e-16] [1.00000000e+00 2.49760836e-25] [7.62630220e-01 2.37369780e-01] [3.47479627e-05 9.99965252e-01] [2.66075292e-11 1.00000000e+00] [5.88493563e-10 9.99999999e-01] [9.71326867e-09 9.99999990e-01]] Predict -> [1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1] 10개 샘플중 4개가 틀림 Y_test[:10] -> [1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1] The accuracy is: 71.6% |
'data science > Artificial Intelligence' 카테고리의 다른 글
| K-Neighbors Classifier (0) | 2025.04.02 |
|---|---|
| Naïve Bayes (나이브 배이스) Classifier - ROC curve (0) | 2025.03.11 |
| Naïve Bayes (나이브 배이스) Classifier - 실전 1 (0) | 2025.02.14 |
| Naïve Bayes (나이브 배이스) Classifier (0) | 2025.02.09 |
| 바이너리 분류 모델에 있어서 평가 항목 (0) | 2024.01.16 |